As you get more and more protons you need more neutrons. Protons are positively charged so they should get repelled however the majority of the nuclei are stable hence there must be certain factors which affect nuclear stability.

Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reaction Neutrons Nuclear
X 3 X 2 2 3 H e T are quite exception.

. It is the most important aspect in determining nucleus stability. They have a neutronproton ratio between 11 and 15. Nuclear Stability is a concept that helps to identify the stability of an isotope.
In the nucleus two forces are battling for dominance - the repulsion of the protons due to the electric force and the attractive nature of the strong nuclear force that draws protons and neutrons together. Is usually that. To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutronproton NZ.
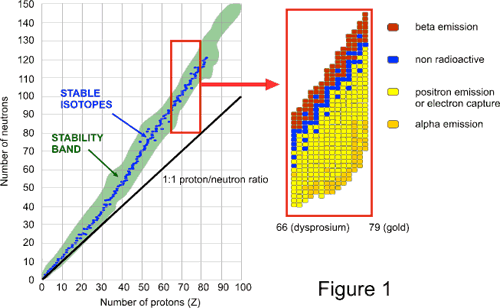
The nuclei in the zone of stability also known as the belt of stability are stable. The following factors have an effect on nucleus stability. The graph below is a plot of the number of neutrons versus the number of protons in various stable isotopes.
Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides known as a. An isotope is called unstable if it has a ratio of protons to neutrons that is not within the band of stability. 3 News of superheavy elements arrive almost everyday.
As the nucleus gets bigger the electrostatic repulsions between the protons gets weaker. An unstable isotope undergoes transmutation alpha decay or beta decay. Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides known as.
This ratio is close to 1 for atoms of elements with low atomic numbers of less than about 20 protons. How is nuclear stability related to the neutronproton ratio in a nuclide. Hence the nucleus is unstable if the neutron-proton ratio is less than 1.
Stability of an isotope can be determined by calculating the ratio of neutrons to protons present in a nucleus NZ. To identify the stability of an isotope it is needed to find the ratio of neutrons to protons. The N to Z ratio turns out to be 15 so as you increase in Z so as you go above Z is equal to 20.
Elements having atomic numbers greater than 70 are never stable. Overview of Nuclear Stability. A certain number of neutrons is needed to offset this repulsive force.
The neutronproton ratio NZ ratio or nuclear ratio of an atomic nucleus is the ratio of its number of neutrons to its number of protonsAmong stable nuclei and naturally occurring nuclei this ratio generally increases with increasing atomic number. This decreases their repulsions but if there are too many neutrons the nucleus is again out of balance and decays. You need more neutrons and lets think about why.
Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides known as a. Adding extra neutrons increases the space between the protons. The stable nuclei are in the pink band known as the belt of stability.
Nucleons with high binding energy are more stable. And after this this is the very first photograph. As the number o protons in a nucleus increases the repulsive force becomes freater than the nuclear force.
Mass defect and binding energy. Nuclear stability makes certain isotopes radioactive. As you increase the number of protons the ratio changes for a stable nucleus.
This is because electrical repulsive forces between protons scale with distance differently than strong nuclear force attractions. The nuclear stability is found to be related to the neutronproton np ratio. Neutron to proton ratio The ratio of neutrons to protons np is a successful way in predicting nuclear stability.
While much of the nature of this strong interaction is still being worked. The neutron to proton ratio NZ ratio. To identify the stability of an isotope it is needed to find the ratio of neutrons to protons.
The np ratio steadily increases as the atomic number increases past element 20 calcium to about element 84 polonium. Mention the factors affecting stability of Nucleus. Think about photograph previously mentioned.
It defines the stability of an isotope of the elements. If for different elements the number of neutrons is plotted against the number of protons it is found that the elements with stable nuclei non-radioactive elements lie within a region. Elements having atomic number less than 20 mostly have proton and neutron ratio 11.
Inspirational How is Nuclear Stability Related to the Neutron Proton Ratio Allowed to my website in this particular moment I am going to show you regarding how is nuclear stability related to the neutron proton ratio. Nuclear Stability is a concept that helps to identify the stability of an isotope. Vii Neutron-proton ratio and nuclear stability or causes of radioactivity.
To identify the stability of an isotope it is needed to find the ratio of neutrons to protons. After the calcium isotope Z 20 all other stable nuclei have a higher neutron-to-proton ratio N Z which increases steadily to about 15 for the heaviest nuclei. Some of the factors that affect nuclear stability are.
Nuclear Stability is a concept that helps to identify the stability of an isotope. Nuclei too aside from this ratio See Valley of stability are unstable undergoing beta decay electron or positron emission or electron capture toward the. Regardless of the number of neutrons however all elements with Z 83 are unstable and radioactive.
Neutron-proton Ratio or n p Ratio. The number of neutrons increases as. To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutronproton NZ.
For light nuclei till about 40 nucleons the neutronproton ratio of stable isobars the same nucleon count is generally around 10. It comes down to a consideration of attractive and repulsive forces acting within the nucleus. 1 or greater than 1.
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutronproton NZ. The most stable nuclei have a neutron proton ratio of.
Explain How The Neutron Proton Ratio Is Associated With The Stability Of Two Nuclei Why Is A Certain Ratio Needed Socratic

How Is Nuclear Stability Related To The Neutron Proton Ratio Brainly In

Neutron Proton N P Ratio As An Indicator Of Nuclear Stability Youtube
0 Comments